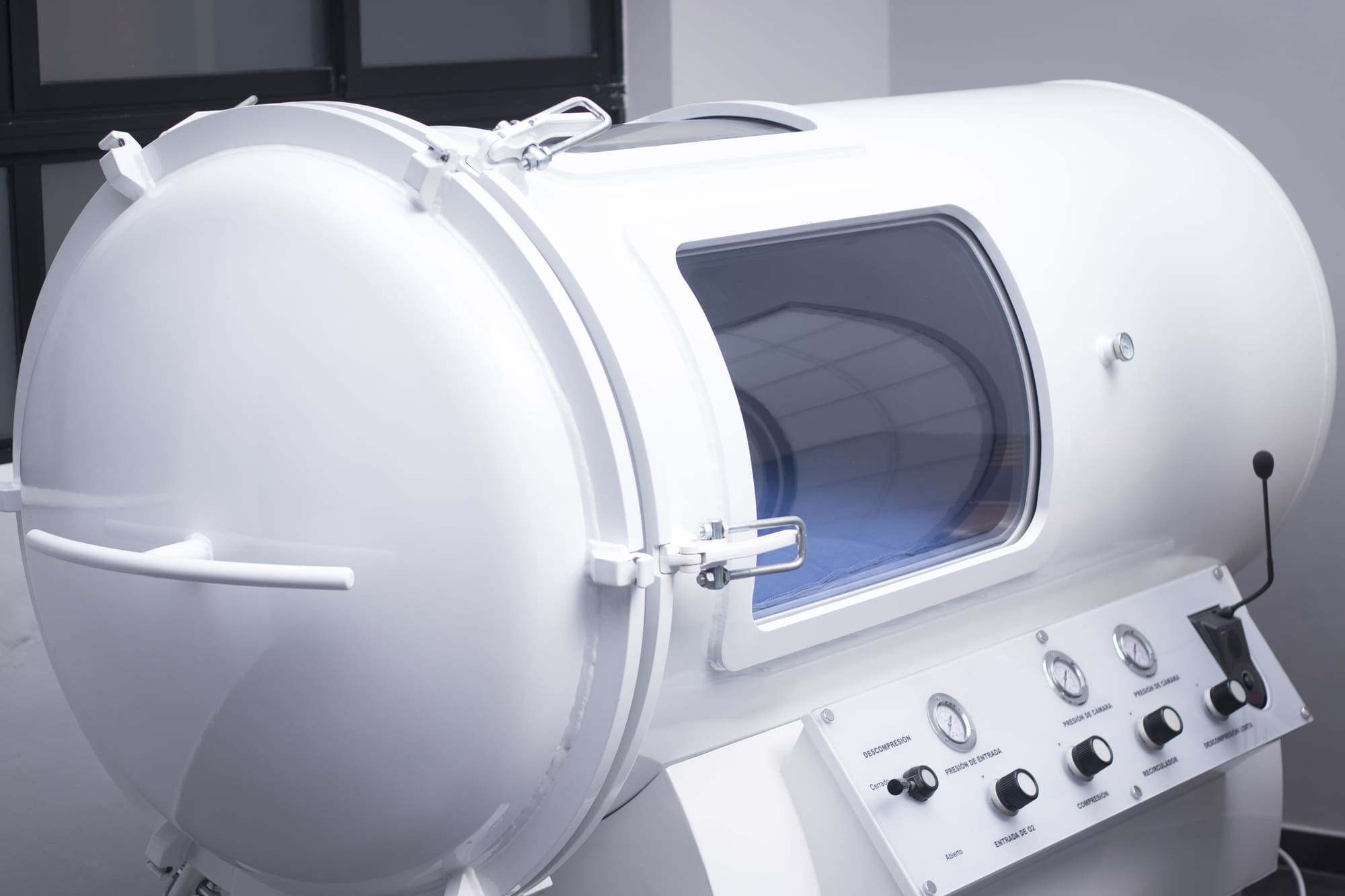
When it comes to recovering from a stroke, traditional therapy methods can only do so much. But what if there was a treatment that could significantly improve outcomes for stroke victims? Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is a cutting-edge treatment that has shown promise in helping stroke victims regain function and improve their quality of life.
Strokes are a leading cause of disability worldwide, with survivors often facing long and challenging roads to recovery. While traditional therapy methods such as physical and occupational therapy are essential, new treatments like HBOT are offering hope for improved outcomes.
In recent years, HBOT has gained attention for its ability to enhance recovery in stroke victims by increasing oxygen levels in the brain and promoting the growth of new blood vessels.
Research has shown promising results, but there is still much to learn about the potential benefits of this therapy. By exploring the intersection of pressurized oxygen environments and stroke rehabilitation, a deeper understanding of how HBOT may positively impact recovery outcomes emerges.
Let's go ahead and explore the potential of HBOT in treating stroke victims and aiding in their recovery.
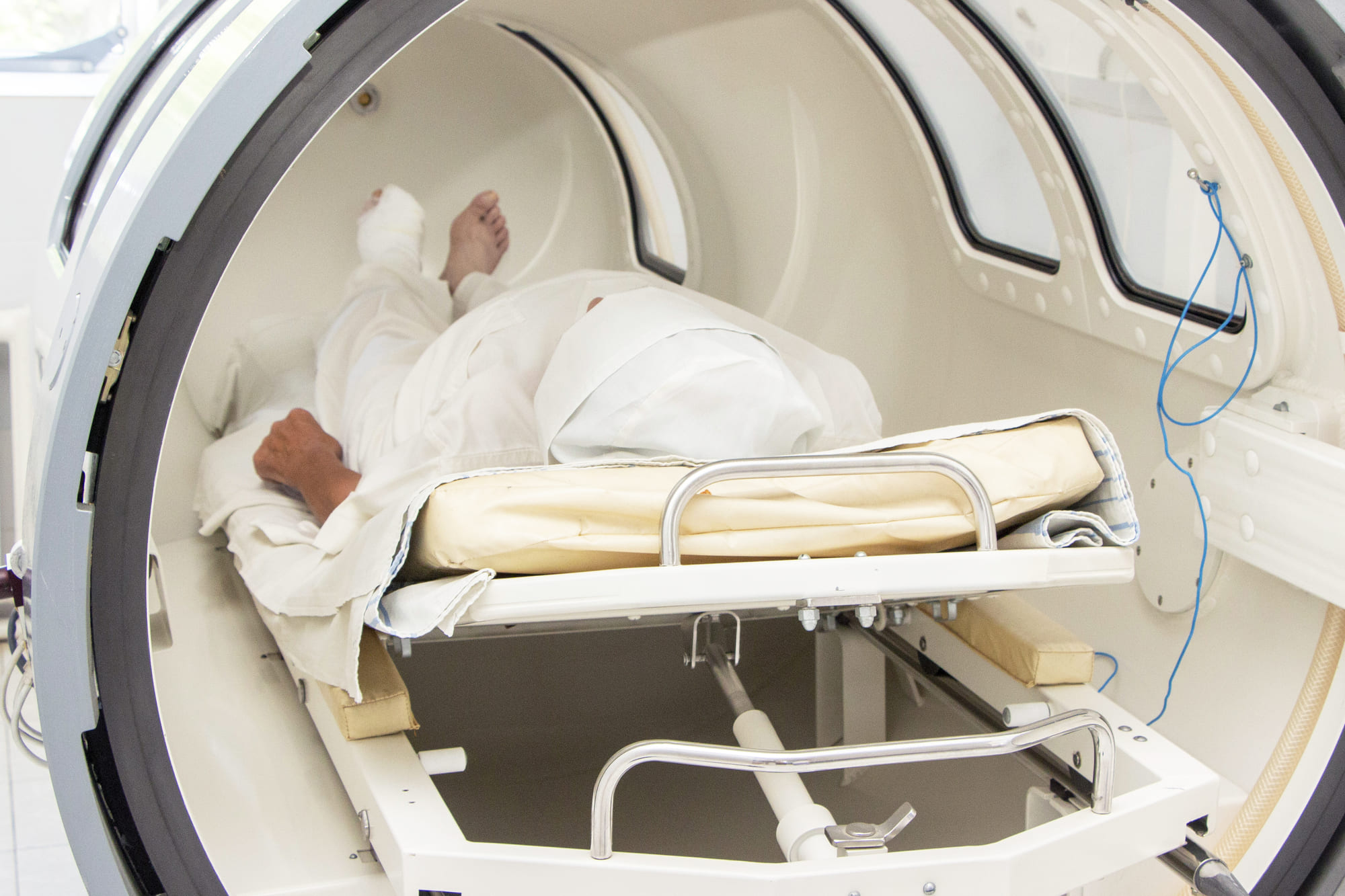
Defining Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy and Its Uses
What is a Hyperbaric Chamber?
Diving Into the Definition of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy entails a patient inhaling pure oxygen within a pressurized chamber, enabling the lungs to absorb more oxygen than usual. This heightened oxygen concentration in the blood offers various advantages, including accelerating wound healing and injury recovery, as well as potentially combatting specific infections.
Recent studies have unveiled additional benefits of hyperbaric oxygen therapy, such as increasing energy levels, enhancing athletic performance, and promoting overall well-being.
By comprehending the applications and impacts of hyperbaric oxygen therapy, individuals can make informed decisions about integrating this treatment into their healthcare regimen, empowering themselves or any patient in the process.
The Medical Conditions HBOT Is Proven to Treat Successfully
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) has gained FDA approval for a wide range of medical treatments, supported by decades of research and successful application in various conditions. HBOT has been approved and is clinically used for several medical conditions, including, but not limited to:
- Crush injury and other acute traumatic ischemias
- Diabetic wounds from high blood sugar.
- Carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Retinal artery occlusion.
- Severe burns.
- Fighting bone infections.
- Healing soft tissue radionecrosis (damage to tissue from radiation therapy.)
- Refractory osteomyelitis.
- Severe anemia when blood transfusions aren't viable.
- Air or gas embolism.
- Decompression sickness
- Failed skin grafts or flaps.
- Soft tissue infections.
The proven benefits of HBOT go beyond these applications, extending to improved circulation, enhanced immune response, and accelerated healing processes.
Studies have also proved that repeated but periodic exposure to high levels of oxygen has been demonstrated to trigger physiological regenerative processes typically associated with hypoxia, meaning
These effects include the formation and repair of neurons (neurogenesis), the proliferation of stem cells, and the development of new blood vessels (angiogenesis).
What Happens During a Stroke: A Definition and Symptoms
As defined by Jickling et al. in 2014, a stroke is a "sudden loss of blood supply to brain tissue resulting from either hemorrhagic or ischemic pathology causing severe neurological deficit" or brain cell damage.
Although the symptoms can vary widely, several symptoms are present in a large percentage of cases, as reported mostly by post stroke patients:
- Sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, particularly on one side of the body.
- Confusion, trouble speaking, or difficulty understanding speech.
- Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes.
- Difficulty walking, dizziness, loss of balance, or lack of coordination.
- Instant, severe headache with no known cause.
It is important to note that some stroke victims may not experience any symptoms at all, a condition known as a silent stroke. These individuals may not realize they have had a stroke until days, weeks, or even months later, when the damage becomes evident.
This is why it is crucial to be aware of the risk factors for stroke and to seek medical attention immediately if any of the above symptoms are present.
The Two Main Types of Strokes: Hemorrhagic and Ischemic Strokes
Broadly, two main types can occur: hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes.
Hemorrhagic strokes happen when a weakened blood vessel ruptures, causing bleeding in the brain. They are overwhelmingly fatal, which is why a smaller share of post-stroke patients are survivors of this type of trauma.
Ischaemic strokes, on the other hand, occur when a blood clot blocks a blood vessel in the brain, cutting off blood flow.
Both a hemorrhagic and an ischemic stroke, if survived, can result in serious complications for individuals, leading to long-term disabilities that can include intense physical and mental therapy that can do little to regenerate the damaged tissue at the core of the problem.
Among the most common long-term complications from stroke on victim's quality of life and health are:
- Paralysis or weakness on one side of the body.
- Difficulty with coordination and balance.
- Cognitive impairments, such as memory loss or difficulty in problem-solving.
- Speech and language difficulties.
- Emotional changes, including depression and anxiety.
- Swallowing difficulties leading to aspiration pneumonia.
- Chronic pain or numbness.
- Fatigue and decreased energy levels.
- Bladder or bowel control problems.
- Increased risk of recurrent strokes or other cardiovascular diseases.
It is because of how damaged brain tissue plays a large part in these disabilities that hyperbaric oxygen therapy is being explored as a potential stroke recovery treatment and therapy for stroke patients.
What The Current Research Says About Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Stroke Patients
In recent clinical studies investigating the efficacy of hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) for post-stroke patients, promising results have emerged, shedding light on the potential benefits of enhancing recovery outcomes.
HBOT involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized room, which allows high levels of oxygen to dissolve into the bloodstream and reach areas of the brain affected by stroke. Research indicates that this increased oxygen delivery may help reduce inflammation, promote the growth of new blood vessels, and support the brain's natural healing processes following a stroke.
For example, one of the most recent and comprehensive studies about this was conducted in Israel in 2020. It showed that HBOT generated significant improvements in all "cognitive domains, even in the late chronic stage" in the vast majority of 162 post-stroke patients who were suffering chronic stroke involved in the study.
Another meta-study found that a wide variety of methods and protocols of hyperbaric oxygen treatment can have benefits, and those benefits extend even into priming stroke-affected tissue into receiving neural stem cells for further recovery.
This other study from Israel in 2013 revealed the vast help that HBOT provided the body with an increased ability of "neuroplasticity," which refers to the nervous system's ability to reroute pathways, heal, and find ways to compensate for damaged tissue. The end result made it clear: "The neurological functions and life quality of all patients in both groups were significantly improved following the HBOT sessions, while no improvement was found during the control period of the patients in the cross group."
So, study after study indeed shows that HBOT can potentially improve neurological outcomes with regard to motor function, cognitive abilities, and overall quality of life for survivors. By providing the brain with the oxygen it needs to repair and regenerate damaged tissue, HBOT shows promise as a complementary treatment for stroke recovery.
Further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms behind HBOT's benefits and to optimize treatment protocols for stroke patients seeking to improve their outcomes and quality of life.
The Benefits of HBOT on Stroke Survivors
We've now established that recent studies have highlighted the significant benefits that hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) can offer to stroke survivors in enhancing their recovery outcomes.
So, to summarize, the effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), which has been found to offer several benefits to stroke survivors, include:
1. Improved oxygen delivery to the brain: HBOT increases the amount of oxygen that can be dissolved in the blood, which can help deliver more oxygen to damaged areas of the brain, promoting healing and recovery.
2. Reduced inflammation: HBOT has anti-inflammatory effects that can help reduce brain swelling and inflammation following a stroke, potentially minimizing further damage.
3. Enhanced neuroplasticity: HBOT may stimulate the brain's ability to reorganize and form new neural connections after such a traumatic brain injury, supporting recovery of lost function after a stroke.
4. Angiogenesis: HBOT can promote the growth of new blood vessels in the brain, improving blood flow to damaged areas and supporting brain tissue repair.
Some of the specific long-term complications or effects of stroke that HBOT can help treat include:
- Chronic fatigue: HBOT can help improve energy levels and reduce fatigue in stroke survivors.
- Cognitive impairment: HBOT has been shown to enhance cognitive function and memory in some stroke survivors.
- Chronic pain: HBOT may help reduce pain levels in stroke survivors experiencing neuropathic pain or other types of chronic pain.
- Motor deficits: HBOT may help improve motor function and coordination in stroke survivors, aiding in physical rehabilitation.
Overall, while more research is needed to fully understand the benefits of HBOT for stroke survivors, current evidence suggests that it may offer a promising adjunctive therapy to conventional stroke rehabilitation programs.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does It Take to See Results from HBOT?
Research findings suggest that stroke victims undergoing hyperbaric oxygen therapy may start noticing improvements in their condition within a few weeks of starting the treatment. These improvements can manifest in various ways, such as enhanced recovery outcomes, improved cognitive functions, and stabilized blood pressure levels.
The effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on stroke victims are believed to be due to the increased oxygen levels in the blood, which can help in supporting brain tissue repair and function. Patients often report feeling more alert and experiencing better overall well-being as they progress through their hyperbaric oxygen therapy sessions.
Monitoring these changes and the overall progression of the patient's condition is crucial in assessing the effectiveness of the treatment in improving the outcomes for stroke victims.
Is blood flow increased to the brain with HBOT?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy has been shown to significantly increase blood flow to the brain, a crucial factor in supporting the potential benefits for stroke victims undergoing this treatment. By exposing the body to increased atmospheric pressure within a hyperbaric chamber, more oxygen dissolves in the blood, leading to higher oxygen levels reaching the brain.
This heightened oxygen delivery can aid in improving the condition of brain tissues affected by stroke, potentially enhancing the healing process and overall outcome for the individual. The increased pressure helps the blood carry more oxygen, which is essential for cellular function and repair.
Therefore, this improved blood flow to the brain is a key mechanism by which hyperbaric oxygen therapy may positively impact stroke recovery.
Who cannot use hyperbaric oxygen therapy?
If you are pregnant, have a history of spontaneous pneumothorax, or suffer from specific untreated lung conditions, it is recommended to avoid HBOT. Individuals with uncontrolled high fevers, claustrophobia, or those who have recently undergone ear surgery may also need to forgo hyperbaric oxygen therapy sessions.
Furthermore, if you have a history of seizures or are under the influence of alcohol or drugs, it is advisable to steer clear of HBOT.
Ensuring your safety and overall well-being is of utmost importance when determining whether hyperbaric oxygen therapy is suitable for you.
Any Potential Disadvantages of Oxygen Therapy for Stroke Patients?
While hyperbaric oxygen therapy shows promise in aiding stroke recovery, there are some considerations to keep in mind. One potential disadvantage is the risk of oxygen toxicity, which can occur if the therapy is administered at high pressures for extended periods.
Typically, HBOT treatment is done at 2.5 atmospheres (ATM) for an hour to an hour and a half each session, but this can vary depending on each treatment facility. Anything above that 2.5 limit can lead to oxygen toxicity, increase oxidative stress throughout the body, and even increase the risk of seizures in some patients, which is why patients with a risk of them are not recommended for HBOT.
Additionally, some individuals may experience discomfort in their ears or sinuses during the treatment due to the changes in pressure.
It's crucial for healthcare providers to carefully assess each patient's suitability for hyperbaric oxygen therapy to minimize any potential risks. Despite these drawbacks, when used appropriately and under professional supervision, oxygen therapy can still offer significant benefits in the rehabilitation process for stroke victims.
Talk to Your Healthcare Provider About Hyperbaric Chamber Therapy for Stroke Patients
The research findings on hyperbaric oxygen therapy for stroke victims highlight its potential benefits in enhancing rehabilitation outcomes.
Recent studies have supported the therapeutic advantages of HBOT in promoting tissue repair and neuroplasticity post-stroke. Integrating HBOT into stroke rehabilitation protocols may offer significant advantages in improving recovery and overall quality of life for individuals recovering from a stroke. If you are a post stroke patient, then it might be worthwhile to discuss this with your healthcare provider or physician.

What is Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy, also known as HBOT, is a wellness therapy in which a person breathes pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber. This therapy is typically administered in a hyperbaric chamber, which can be a monoplace chamber designed for a single person or a multiplace chamber that can accommodate multiple individuals. The chamber is pressurized to levels higher than atmospheric pressure, usually around 2 to 3 times normal atmospheric pressure. The primary mechanism of action of HBOT is to increase the amount of oxygen dissolved in the bloodstream, which can promote various therapeutic effects.
Sessions usually last between 30 minutes and 2 hours, and frequency can vary depending on the specific concern being treated and the recommendations of the recipient's wellness advisor(s). In many cases, a standard course of treatment involves daily sessions, typically five days a week. The suggested total number of sessions can range from just a few to several weeks' worth, depending on the nature and severity of the issue the recipient seeks to address.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Benefits
- Increases Blood Oxygen Levels
- Stimulates Growth Factors and Stem Cells
- Improves White Blood Cell Activity
- Decreases the Size of Blood Oxygen Molecules and Increases Circulation
- Increases ATP Energy Molecule Production
- Stimulates Blood Vessel Synthesis and Proliferation
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Applications
Wound Healing
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy can promote the healing of certain wounds, such as diabetic foot ulcers, non-healing surgical wounds, wounds resulting from traumatic injuries, and burns. In conditions like trauma-induced crush injuries, this works by increasing the amount of dissolved oxygen in the bloodstream through higher pressure. It also reduces bubble size and promotes various healing processes, including vasoconstriction to manage tissue swelling, collagen synthesis for wound healing, and angiogenesis for new blood vessel formation. Simultaneously, HBOT enhances the body's defense against bacteria by increasing oxygen free radicals and improving the effectiveness of certain antibiotics.1 Wound healing is common reason people receive HBOT in wellness studio settings such as ReEnergized, and is also widely recognized and implicated in emergency medical settings.
Fighting Infections
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy can also help fight bacterial and fungal infections, including more severe and treatment-resistant infections such as those resulting from diabetic wounds, surgical complications, and radiation-related complications. HBOT is particularly valuable when faced with any of the growing list of antibiotic-resistant pathogens, for those allergic or intolerant of antibiotics, and for anyone avoiding the overuse of antibiotics as a means of optimizing their natural immunity. Specifically, HBOT fights infection by slowing down or killing bacteria and boosting the immune system's natural ability to fight infections. Additionally, it works well alongside other infection-fighting treatments as a complimentary approach.2
Radiation Injury
Cancer patients often undergo hyperbaric oxygen therapy to reduce the side effects of radiation treatment on healthy tissues. These include thermal burns and the potentially-fatal sepsis infection than can result from them. HBOT has an extensive history of success in treating burns– in fact, scientists have known of its ability to reduce burn healing times and mortality rates for over half a century.3 While HBOT is known to treat infections like sepsis by fighting bacteria and boosting immunity, it treats burns by increasing the O2 levels in burned tissues.3
Treating Herpes Family Viruses
Common viruses in the herpes family include herpes varicella-zoster (chickenpox), herpes zoster (shingles), herpes simplex types I and II, and herpes meningitis. Like many viruses, they are anaerobic, meaning they thrive in environments without oxygen. By increasing bodily oxygen content and circulation, hyperbaric oxygen therapy has been shown to drastically accelerate herpes blister and lesion healing, relieve associated pain, and reduce the prevalence of certain symptoms associated with some herpes strains, such as neuralgia and depression.4
Treating Traumatic Brain Injury
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy has been demonstrated in numerous studies to have neuroprotective properties when administered to sufferers of traumatic brain injuries (TBI). It does this by improving preventing cell death, reducing inflammation, improving tissue oxygenation and cellular metabolism, and promoting the formation of new neurons and blood vessels in the brain.5
Treatment of Decompression Sickness and Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
One traditional application of hyperbaric oxygen therapy is to treat decompression sickness, also known as nitrogen gas embolism or 'the bends.' Decompression sickness is most commonly caused by ascending too rapidly after scuba diving, which leads to nitrogen gas bubble to formation within the affected person's blood vessels. Left untreated, decompression sickness can lead to severe side effects such as tissue damage, stroke, or heart attack, and can even be fatal.6 The pressurized environment in the hyperbaric chamber allows the increased atmospheric pressure to force more oxygen into the bloodstream, which helps to shrink, dissolve and eliminate the gas bubbles there. Simultaneously, the increased oxygen availability helps to support tissues that may be experiencing oxygen deprivation due to the blockage caused by gas embolisms. These are the same mechanisms by which HBOT speeds the removal of the noxious gas carbon monoxide from the bloodstream.
Treatment of Vascular Air Embolism
In contrast to decompression sickness, vascular air embolism (or VAE) occurs when the bubbles formed in the affected person's arteries are made up of air, as opposed to nitrogen. This usually occurs as a side effect of some routine medical procedures, such as the administration of fluids intravenously.7 The mechanisms by which HBOT treats gas embolisms and vascular air embolisms are generally similar. Both conditions involve the presence of gas bubbles in the bloodstream, which can obstruct blood vessels and lead to tissue damage. For both types of embolisms as well as carbon monoxide poisoning, HBOT should be administered in a timely manner for the best chance at preventing severe consequences, and treatment should not be completed before first receiving professional guidance from the recipient's emergency healthcare team.6, 7
Types of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
If you're interested in hyperbaric oxygen therapy, you're probably wondering how someone receives this treatment. HBOT is usually administered in one of three different types of settings:
- Wellness Studios: Many wellness studios and holistic health practitioners offer hyperbaric oxygen treatments on their menus. Common reasons people seek treatment from these independent health centers include their desire to treat various infections, facilitate wound or injury healing, facilitate collagen formation, and to treat the symptoms of herpes viruses. You can search online or call nearby locations to see if they offer hyperbaric oxygen therapy and ask about pricing and availability.
- Clinical Medical Providers: Some hospitals, medical offices and clinics also offer HBOT as a treatment for certain conditions, such as non-healing wounds, severe infections resistant to conventional treatment methods, noxious gas poisoning, vascular gas embolism or decompression sickness, traumatic brain injuries, and gangrene. In this case treatment is either administered in an emergency setting, or the patient receives a referral from their primary care doctor to see a specialist.
- At-Home Devices: Of course, there are some who prefer the convenience of receiving chamber therapies at home, and have the necessary space and funds to invest in their own machine. While this option can be attractive, be forewarned– if inadequate training or insufficient focus lead to improper use, the consequences can be serious.8 Additionally, these at-home devices are usually inflatable rather than solid fixtures, and are typically smaller and less powerful than the ones used in professional settings. However they can still be effective for certain conditions.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Risks
The risks associated with hyperbaric oxygen therapy are generally considered to be rare when the treatment is administered appropriately by qualified, informed professionals. These include potential claustrophobia while laying in the chamber, anxiety, lightheadedness, fatigue, ear or sinus pressure or discomfort, and in cases where the recipient was in the chamber for too long, there have been cases of oxygen poisoning. HBOT is not recommended for pregnant women or individuals with middle ear barotrauma, uncontrolled high blood pressure, or acute or chronic respiratory conditions.
References
1. Hyperbaric oxygen and wound healing
2. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: Antimicrobial mechanisms and clinical application for infections
3. Treatment of burns with hyperbaric oxygen (Article)
4. Effect of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on patients with herpes zoster
5. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for traumatic brain injury: bench-to-bedside
8. Safety Precautions for HBOT at Home: What You Need to Know
Get In Contact
Call
Location
4434 E Pacific Coast Highway
Long Beach, California 90804
Hours
Monday - Friday
11:00AM - 07:00PM
Saturday - Sunday
11:00AM - 04:00PM
Get In Contact
Call
Location
4434 E Pacific Coast Highway
Long Beach, California 90804
Hours
Monday - Friday
11:00AM - 07:00PM
Saturday - Sunday
11:00AM - 04:00PM